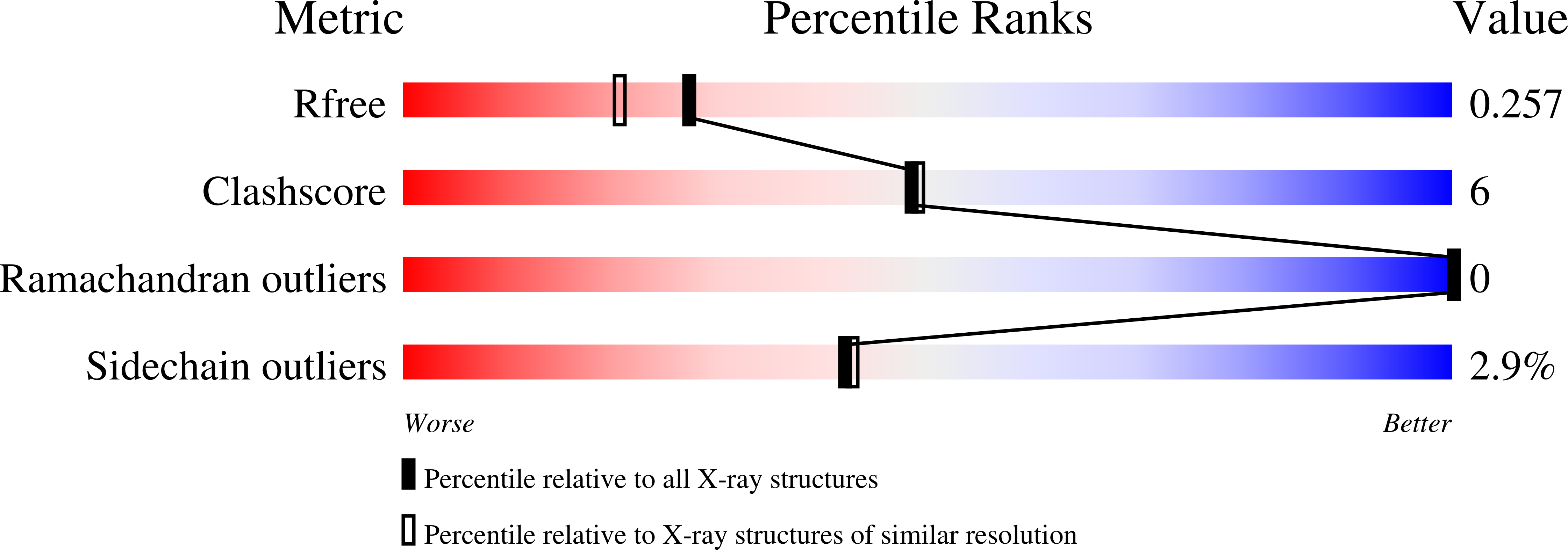ARAF mutations confer resistance to the RAF inhibitor belvarafenib in melanoma.
Yen, I., Shanahan, F., Lee, J., Hong, Y.S., Shin, S.J., Moore, A.R., Sudhamsu, J., Chang, M.T., Bae, I., Dela Cruz, D., Hunsaker, T., Klijn, C., Liau, N.P.D., Lin, E., Martin, S.E., Modrusan, Z., Piskol, R., Segal, E., Venkatanarayan, A., Ye, X., Yin, J., Zhang, L., Kim, J.S., Lim, H.S., Kim, K.P., Kim, Y.J., Han, H.S., Lee, S.J., Kim, S.T., Jung, M., Hong, Y.H., Noh, Y.S., Choi, M., Han, O., Nowicka, M., Srinivasan, S., Yan, Y., Kim, T.W., Malek, S.(2021) Nature 594: 418-423
- PubMed: 33953400
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03515-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XFP - PubMed Abstract:
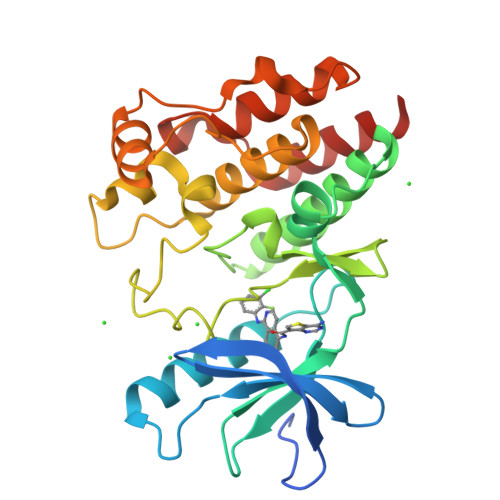
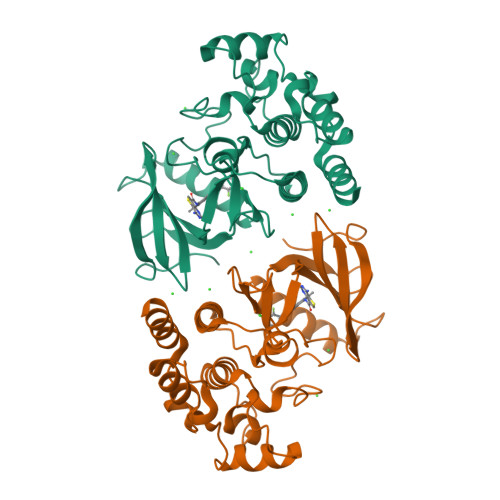
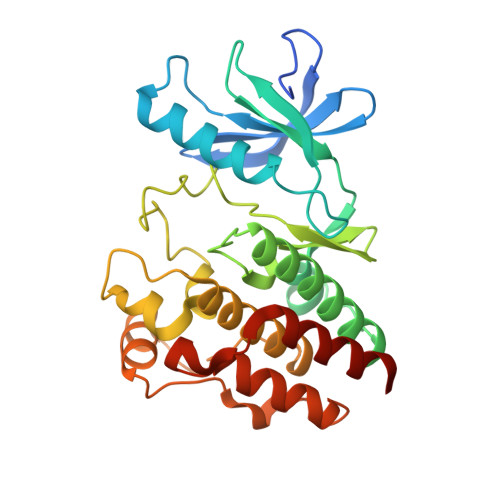
Although RAF monomer inhibitors (type I.5, BRAF(V600)) are clinically approved for the treatment of BRAF V600 -mutant melanoma, they are ineffective in non-BRAF V600 mutant cells 1-3 . Belvarafenib is a potent and selective RAF dimer (type II) inhibitor that exhibits clinical activity in patients with BRAF V600E - and NRAS-mutant melanomas. Here we report the first-in-human phase I study investigating the maximum tolerated dose, and assessing the safety and preliminary efficacy of belvarafenib in BRAF V600E - and RAS-mutated advanced solid tumours (NCT02405065, NCT03118817). By generating belvarafenib-resistant NRAS-mutant melanoma cells and analysing circulating tumour DNA from patients treated with belvarafenib, we identified new recurrent mutations in ARAF within the kinase domain. ARAF mutants conferred resistance to belvarafenib in both a dimer- and a kinase activity-dependent manner. Belvarafenib induced ARAF mutant dimers, and dimers containing mutant ARAF were active in the presence of inhibitor. ARAF mutations may serve as a general resistance mechanism for RAF dimer inhibitors as the mutants exhibit reduced sensitivity to a panel of type II RAF inhibitors. The combination of RAF plus MEK inhibition may be used to delay ARAF-driven resistance and suggests a rational combination for clinical use. Together, our findings reveal specific and compensatory functions for the ARAF isoform and implicate ARAF mutations as a driver of resistance to RAF dimer inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Discovery Oncology, Genentech Inc., South San Francisco, CA, USA.